-
Excited-state symmetry breaking in 9,10-dicyanoanthracene-based quadrupolar molecules: the effect of donor-acceptor branch length
Z. Szakács, F. Glöcklhofer, F. Plasser and E. Vauthey
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 23 (2021), p15150-15158


DOI:10.1039/D1CP02376D | unige:153776 | Abstract | Article HTML | Article PDF | Supporting Info
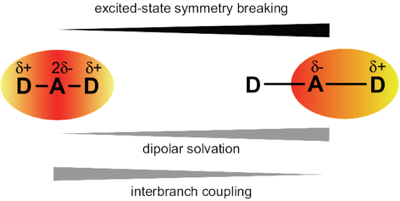
Excited-state symmetry breaking is investigated in a series of symmetric 9,10-dicyanoanthracenes linked to electron-donating groups on the 2 and 6 positions via different spacers, allowing for a tuning of the length of the donor-acceptor branches. The excited-state properties of these compounds are compared with their dipolar single-branch analogues. The changes in electronic structure upon their optical excitation are monitored by transient electronic spectroscopy in the visible and near-infrared regions as well as by transient vibrational spectroscopy in the mid-infrared. Our results reveal that, with the shortest branches, electronic excitation remains distributed almost symmetrically over the molecule even in polar environments. Upon increasing the donor–acceptor distance, excitation becomes unevenly distributed and, with the longest one, it fully localises on one branch in polar solvents. The influence of the branch length on the propensity of quadrupolar dyes to undergo excited-state symmetry breaking is rationalised in terms of the balance between interbranch coupling and solvation energy.